歡迎您來到深圳欣博盛生物科技有限公司網(wǎng)站!
歡迎您來到深圳欣博盛生物科技有限公司網(wǎng)站!
更新時間:2022-01-28
CYTO-ID® Autophagy Detection Kit measures autophagic vacuoles and monitors autophagic flux in lysosomally inhibited live cells using a novel dye that selectively labels accumulated autophagic ……
No transfection required
Proprietary dye includes titratable moieties specific for selectively staining autophagic vesicles
Protocol validated with known inhibitors and activators of autophagic activity
Rapidly quantifies autophagy in native heterogeneous cell populations
Eliminates need for time and effort-consuming transfection efficiency validation required with LC3-GFP transfection
Selective and comprehensive staining, allows measurement and differentiation between autophagic flux and autophagolysosome accumulation
Negligible staining of lysosomes reduces background seen with other dyes
Facilitates high-throughput screening of activators and inhibitors of autophagy




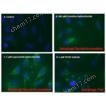
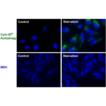

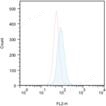


| Applications: | Flow Cytometry, Fluorescence microscopy, Fluorescent detection, HTS |
| Application Notes: | The CYTO-ID® Autophagy detection kit provides a rapid, specific and quantitative approach for monitoring autophagy in live cells by fluorescence microscopy, flow cytometry, and microplate reader. |
| Quality Control: | A sample from each lot of CYTO-ID® Autophagy detection kit is used to stain HeLa Cells as described in user manual. CYTO-ID® autophagy detection reagent is incorporated into induced cells, observed as accumulative typical spherical vacuoles in foci or throughout cytoplasm. Comparing to untreated HeLa cells, treated sample demonstrate significant increase in fluorescence under microscope. |
| Quantity: | For -K200 size: 200 flow cytometry assays, 250 microscopy assays or 3 x 96-well microplate assays. For -0050 size: 50 flow cytometry assays, 60 microscopy assays or 1 x 96-well microplate assays. |
| Use/Stability: | With proper storage, the kit components are stable for one year from date of receipt. |
| Handling: | Protect from light. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Shipping: | Shipped on Blue Ice |
| Short Term Storage: | -20°C |
| Long Term Storage: | -80°C |
| Contents: | CYTO-ID® Green Detection Reagent Hoechst 33342 Nuclear Stain Autophagy Inducer (Rapamycin) Chloroquine Control 10X Assay Buffer |
| Scientific Background: | Autophagy is a stress-induced protective mechanism. Less active under basal conditions, the mechanism is utilized by eukaryotic cells through lysosome-mediated bulk degradation of cellular contents when subjected to certain hostile conditions such as nutrient depletion and chemical or environmental stress. The role of increased autophagic activity in the pathology of cancer, neurodegeneration, cardiovascular disease and diabetes has become widely recognized and commonly studied. Induction of autophagic flux can be visualized by enhanced accumulation of autophagic vesicles if lysosomal function is inhibited, preventing removal of these vesicles. |
| Technical Info/Product Notes: | The CYTO-ID® Autophagy Detection kit is a member of the CELLESTIAL® product line, reagents and assay kits comprising fluorescent molecular probes that have been extensively benchmarked for live cell analysis applications. Featured in: Nature Methods - Autophagy: eat thyself, sustain thyself - Nature Methods, 12.2015 Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology News - HTS Profiling Method for Autophagy-Modulators Application Notes: Autophagy Analysis Using Object Spot Counting Using Gen5 to Analyze the Size and Number of Autophagosomes Per Nuclei Towards Understanding the Molecular Basis of Parkinson’s Disease: Cell-based Model of Mitophagy and Aggresome Accumulation Response Profiles of Known Autophagy-Modulators Across Multiple Cell Lines: Using CYTO-ID® Autophagy Dye to assess Compound Activity and Toxicity Cell-Based Screening of Focused Bioactive Compound Libraries: Assessing Small Molecule Modulators of the Canonical Wnt Signaling and Autophagy-Lysosome Pathways A Novel Image-Based Cytometry Method for Autophagy Detection in Living Cells Predictive High-Content/High-Throughput Assays for Hepatotoxicity Using Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell (iPSC)-Derived Hepatocytes Visualizing subcellular vesicles to quantitate autophagy in neuronal cells Cited samples: For an overview on cited samples please click here. |
| Protocol: | A detailed protocol for FC in primary BMDCs can be found on bioprotocol.org: Flow Cytometric Analysis of Autophagic Activity with CYTO-ID Staining in Primary Cells by M. Stankov, et al. |
| Regulatory Status: | RUO - Research Use Only |
如需購買或咨詢該產(chǎn)品技術(shù)問題,請聯(lián)系ENZO一級代理商-欣博盛生物